The road to digital simulation (II) industrial upgrading is the lifeblood of mastering the future
Ma Caoyuan
As we all know, SMEs are an important force in China's economy and the backbone of modern economic construction. According to the 2018 State Council statistics, China's small and medium-sized enterprises have the typical characteristics of "five, six, seven, eight, nine": "contribute more than 50% of the tax revenue, more than 60% of GDP, more than 70% of technological innovation, more than 80% of urban labor employment, more than 90% of the number of enterprises. " Therefore, compared to large enterprises, SMEs are the main victims of this pandemic. Among the SMEs, a large number of manufacturing enterprises related to machine manufacturing and equipment manufacturing are even worse, not only in procurement, production, manufacturing, sales and other aspects of the fatal blow, the resulting financial pressure should not be underestimated.
As of the date of writing, there are 68,584 confirmed cases, 8,228 suspected cases, 11,272 severe cases, 1,666 deaths and 9,472 cured cases nationwide. In order to minimize the spread of the virus through the movement and gathering of people, the Chinese New Year in 2020 saw a series of extraordinary actions: traffic and movement controls were imposed, a large number of services were closed, holidays were extended, and companies delayed their return to work. While this series of actions minimized the spread of the virus, it also raised concerns about the economic situation.
Impact of the pandemic on the manufacturing sector:
Firstly, labor shortage, weak offline demand and shrinking trade have seriously affected the manufacturing industry.
As a result of the pandemic, localities have implemented quarantine systems one after another, whether or not they are infected areas, which has left many laborers trapped in quarantine zones and unable to return to factories in time for manufacturing. Subjectively, this caused a short-term shortage of labor, which in turn affected the short-term production of the manufacturing industry, and companies encountered problems such as labor shortage and difficulty in returning to work.
For example, Shanghai Volkswagen announced that 3,500 employees worked from home for two weeks and were in a work stoppage until February 10. Suzhou and Wuxi also saw a large number of entrepreneurs who had long been in their factories but no workers were on board, and companies were at a production standstill.
Secondly, Chain reactions, production fluctuations, supply chain breakdowns, and capital chain tensions continue to affect the development of the manufacturing industry.
Sales in the fields of film and television, tourism, catering, and clothing were hit hard, with some experts predicting losses during the Spring Festival expected to be around 500 billion yuan. This in turn caused a decline in sales of physical stores, which hit manufacturing companies hard through a chain reaction in the supply chain. Factors such as short-term shortage of labor and weak demand cause abnormal fluctuations in the winning field, which will continue to affect the healthy development of the manufacturing industry.
The liquidity of SMEs through the chain reaction has been hit hard. The impact of the pandemic has reduced monetary liquidity at the social level, which in turn has led to cash flow constraints for SMEs. The backlash due to supply chain transmission and other reasons will in turn have a greater impact on the real economy, increasing corporate losses and job losses.
For example, Bosch Group issued an early warning in early January for China's manufacturing industry, saying that it has 23 factories in China and is highly dependent on Chinese production, and that the pandemic may lead to a risk of disruption in its global supply chain; Sharp said at the conference that it would consider transferring its production operations originally placed in China to other countries and regions if the impact of the pandemic continues to intensify.
China is a large manufacturing country, and a number of manufacturing clusters with special characteristics are clustered in central China and surrounding provinces, represented by Hubei. As a result of this pandemic, the manufacturing industry is facing many challenges such as labor shortage, weak demand and shrinking trade. Not only in Hunan, but also in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Northeast China, the survival of small and medium-sized manufacturing industries is difficult in the face of gradually increasing downward pressure on the economy, with the number of recruitable workers decreasing year by year, costs rising year by year and profits declining year by year. At the same time, according to the National Bureau of Statistics, in 2013, China's new employment population, nearly 43 million people graduated from college, 21.5 million from high school and 21.5 million from junior high school. And the low-end labor force decreased by about 60 million in 2019 compared to 1969, which indirectly affected the shortage of manufacturing manpower.
In response to the economic concerns caused by the pandemicpandemic, the country has introduced many policies to help enterprises overcome economic difficulties, such as giving full play to the advantages of data aggregation, resource dispatching and data analysis to improve the efficiency of emergency disposal in the pandemic, helping manufacturing enterprises to move from offline sales to online and accurately connect with customers, helping manufacturing enterprises to quickly locate upstream suppliers and improve the efficiency of raw material procurement, The company also provides remote office support to reduce the frequency of front-line staff traveling to and from factories, connects financial institutions and manufacturing enterprises to solve the problem of capital tension, and helps enterprises anticipate market changes in advance to improve the level of intelligent decision-making in production business under market fluctuations.
At the same time, from the perspective of non-pandemic, the competitiveness of "Made in China" is obviously declining in the long run, and the demographic dividend is lost.
(1) The number of workers will decrease by 1.55 million per year until 2020, by 7.9 million per year until 2030, and by 8.35 million per year until 2050
(2) Labor costs in China have been rising at an average annual rate of about 10%, and domestic labor costs in China have doubled in five years.
In 2016, labor costs in Southeast Asia were 40% of those in China, and in 2013, China's labor costs surpassed Japan's in terms of unit labor costs.
The above reasons led to a 5%-9% reduction in China's labor cost competitiveness between 2004 and 2014.
(3) China continues to lose young workers (new generation of young people are not willing to work in the field)
The "post-90s" are growing into a new generation of workers The post-90s are characterized by (self-confidence, passion, but lack of patience and low commitment. They also have distinctive characteristics, with big fluctuations in thinking and more direct, often saying that they are not in a good mood, so they do not go to work.
From this we can learn that whether it is from the long-term labor costs caused by the increase in competitiveness, or the short-term impact of the pandemic and the lack of manufacturing enterprises to start work.
The development of automation and intelligent production is our only way out
So, the current status of automation in China:
China's industrial robot import dependence is strong, and Made in China 2025 promotes domestic substitution. China has continued to import industrial robots on a large scale for many years, and from 2011 to 2015, China has been the world's top industrial robot importer for five consecutive years, and the world's top industrial robot importer for five consecutive years, making it a veritable industrial robot importer. in 2015, China's industrial robot imports reached 46,800 units, with a total amount of $805 million. According to the China Robotics Federation, the density of industrial robots used in China was 49 units/10,000 workers in 2015, compared with the global average of 69 units/10,000 workers and as high as 531 units/10,000 workers in South Korea. The lower robot usage density indicates that the level of automation in China's manufacturing industry is still low.
But the biggest trouble in automated production is the automation process and efficiency.
At present, digital factory technology is an effective solution to improve the accuracy of automation process and automation efficiency.
Digital factory: Before and after the mass production of products, the production facilities are audited, planned, verified and monitored in a digital virtual environment in advance. In order to identify problems in advance and propose improvement solutions, and apply them to the field. Thus, we build a digital simulation simulation factory that can guarantee the quality of new products, equipment and mass production.
Significance of digital simulation:
1.Improve production planning efficiency and reduce process planning as well as general product development costs
2.Determine the feasibility of manufacturing by simulating the manufacturing process before starting production
3.Speed up product launch to market by reducing process planning time and time from pilot to mass production
4.Linking product design and manufacturing planning to improve design for manufacturing feasibility
5.Validate and improve product design from a process perspective to improve production quality
6.Use digital simulation and production line simulation to reduce the number of prototypes
7.Improve collaboration across functions within the enterprise and between the enterprise and suppliers
Current status of digital simulation in terms of enterprise size and geographic location:
Large enterprises: inefficient product development due to the absence of digital simulation modules, risk of failure of investment in large projects, lack of simulation talents;
Small enterprises: the price of simulation software is expensive and unaffordable (generally millions/set), the rework of the project many times leads to a sharp increase in costs, the boss bears the risk of failure of subordinates, no simulation engineer available;
Individuals: simulation software can not be purchased genuine, no special training institutions in China, employment difficulties;
International: monopolized by large enterprises such as Siemens Dassault, many domestic research institutions and no large simulation software was born, still stuck in the simulation stage of a single machine or a single workstation;
The above facts must give birth to a set of solutions to reduce the door frame of digitalization and break the current monopoly pattern, that is the birth of digital simulation cloud platform.
In response to this situation, Ningbo Seysoft has developed the DMworks simulation platform to cope with the impact of such an pandemic public emergency and the huge impact on the company, taking advantage of its own industry and in line with national policies.
The following are the specific details of the DMworks platform.
Digital simulation cloud platform: By establishing a hardware resource and software resource environment based on centralization, we provide digital simulation computing and storage services, and users can log in and enjoy digital simulation services at any time without any limitation of terminals. Divided into three pieces:
【1】DMworks simulation technology
1、Introduction of DMworks
(Digital Manufacturing Works) is a factory simulation software, which covers a wide range of robotic production environment from concept development to debugging ideas, design, simulation, verification equipment, and finally evaluate the task of the production line and manufacturing process.
Using DMwoks, users can simply build a complete motion model of the entire manufacturing plant. It allows the perfect introduction of the manufacturing process on the shop floor.
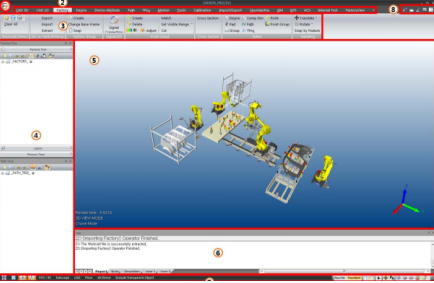
(The picture shows the DMworks operation page)
2. Introduction to CAD
CAD Word provides utilities to prepare the two types of data used in FACTORY WORLD. The two main materials (data) to be processed are "CAD Geometry" and "Simple Device". Each material will have its own hierarchical data tree to manage. Each hierarchical data tree provides its own pop-up menu for creating and manipulating the corresponding material.
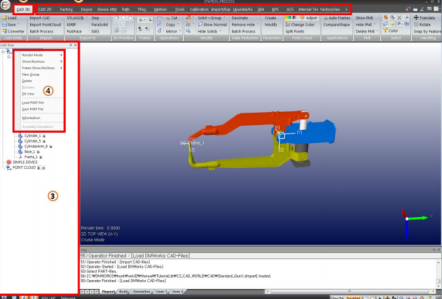
(The picture shows the operation page in CAD mode)
3.Introduction of Factory World
Create, manage, simulate, and validate resources and processes in Factory World. most of the operations and functions in Factory World are provided on the menus popped up by the data trees, and the pop-up functions and operations are consistent with the buttons in the menus.
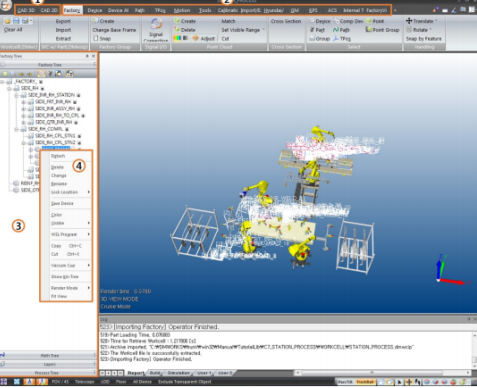
(The figure shows the operation page in CAD mode)
4.Devices
Equipment is the smallest formation in Factory World, which can be prepared for movement in DMworks. Robots, welding guns, conveyors, body panels between and safety nets are examples of equipment.
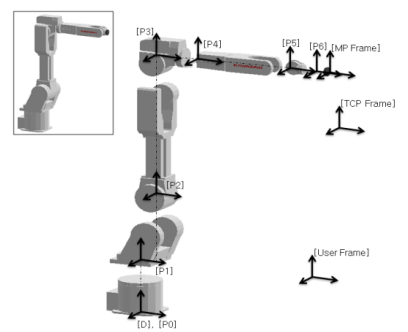
(The diagram shows the disassembly of the equipment)
5.Factory layout and its structure tree
In DMworks, a hierarchical tree of "Factory World" can be used to define the factory. Each grouping represents a set of devices classified by layout and tasks. Each factory can include other self-groups, devices, composite devices, and other related information such as device dependencies, signal connections, etc. A factory grouping can be a station, a production line, a conveyor system, a racking system, or a factory.
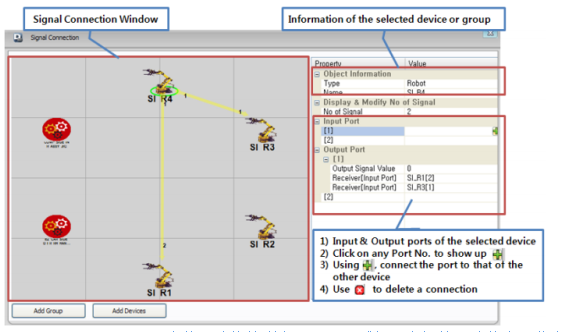
(The figure shows the pop-up window of signal connection for debugging the motion status between machines, this is one of the sub-functions.)
6.Motion and Tasks (Path / Tpos)
If a device has been created and defined, the user can create and simulate the motion of the device, which is used for debugging and simulating the motion of the device.
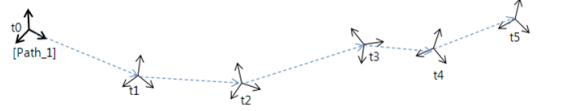
(Figure shows an example of Path/Tpos)
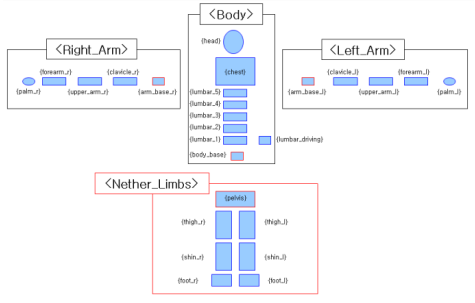
(Figure shows the composition of the basic human model for visualization techniques, as one of the sub-functions)
7.Robot off-line programming
Path/Tpos itself and its properties can be defined and described for the robot's motion, Motion's properties, Tool's movement and action. Users can create, modify and simulate the debugging position and Tool's movement of the robot.

(The figure shows the collision area test of two robots, which is one of the sub-functions)
8.Processes of the workstation
A series of operations performed by a device for a specific purpose becomes "a task of device". As mentioned in Chapter 6, a task of device can be expressed through paths, target locations, and their properties, such as motion properties, and tool behavior. In DMWorks, as described in Chapter 5, factories can be defined using a hierarchical tree of "Factory Groups". A Factory Group can be a workstation, a production line, a conveyor system, or an accompanying fixture system. A "workstation" is the smallest combination of equipment that works together for a common production goal.
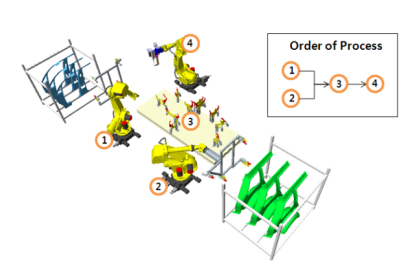
(Figure shows the SIDE_RH plant combination for a workstation process)
DMWorks simulation technology allows companies to know their cost operations and production changes in advance, to control and prevent possible unnecessary cost increases due to risks, to reduce unnecessary labor costs, and to reduce management operating costs. In the current economic downturn pressure remains, the manufacturing industry outlook is not good, who can take the lead in transformation and upgrading, and will own unnecessary cost reduction, who will be able to grasp the right to survive in the future.
【2】Factory and production line scanning technology
Factory scanning uses a large scanner to scan the production line and factory, the scanning radius is generally 180m, and the maximum error of a point is 3mm, and in general, according to the size of the production line and factory, we choose to scan multiple points, and finally group them into a model to control the error within 1mm. The scanned point cloud is shown in [Figure 10

【Figure 10】Point cloud model
Scanning (point cloud) data is very large, it is difficult to run in the general software, and in DMWORKS software on the point cloud data is light, you can achieve in DMWORKS interface while opening the production line or factory point cloud scanning data and 2D layout map for comparison, according to the scan data to theoretical 2D layout one by one adjustment (currently for manual adjustment), to get the real 3D layout layout diagram. As in [Figure 11
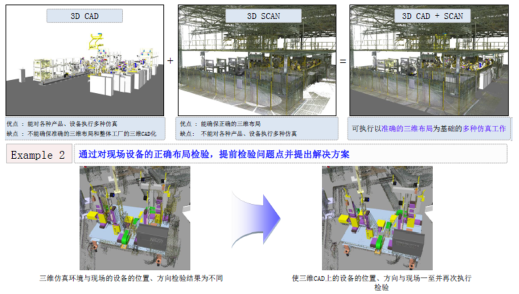
【Figure 11】 Layout adjustment
Through the production line and factory scanning steps to get the real (error ≤ 1mm) 3D production line and factory model, which is very meaningful, otherwise do not get the real digital factory. The 2D & 3D factory layout map with real and realistic error not more than 1mm is very helpful for the future production line planning and factory transformation.
【3】Robot calibration technology
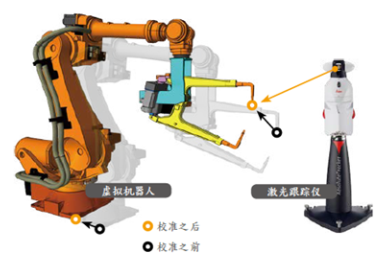
The process of reducing the installation and mechanical kinematic errors between the virtual robot and the actual robot by measuring the actual robot, calculating the robot installation position and orientation, robot tool installation position and orientation, robot TCP position and orientation, and robot mechanical kinematic information, and reflecting it to the simulation software.
Reduce the absolute position error of the robot off-line program (OLP) and shorten the robot's commissioning time
【4】Virtual reality VR technology

(The picture shows entrepreneurs experiencing virtual reality VR technology)
The VR visualization technology developed on the basis of DMWORKS not only gives a visualization space to those bosses who can't concentrate on one thing wholeheartedly because of their busy schedule, but also allows experts to view the layout of the factory without having to go to the site in person, and to see the configuration and composition of the factory equipment at a glance, so that they can make valuable comments on the site and process when the equipment is not yet developed, and reduce unnecessary errors. The VR technology of DMWORKS can also achieve a zero-touch effect on customer experience, allowing important customers to watch the operation of the production line with VR glasses, without having to visit the factory in person, and giving engineers the opportunity to show their skills on the platform. Not only does it offer advantages over traditional layouts, but it also opens up new opportunities for traditional factory design.
Finally, may China survive this pandemic, may the motherland be great and prosperous, and may all entrepreneurs survive this crisis safely and smoothly transform and upgrade.